Overview
dLEND is dTRINITY’s native lending protocol for  dUSD, forked from Aave V3. It serves as the credit engine of the ecosystem, enabling dUSD lending and borrowing activity to take place on Fraxtal (and soon, Ethereum). Similar to Aave, dLEND is a multi-collateral money market, where lenders earn yield by supplying dUSD into a shared pool while others borrow dUSD from that pool by supplying one or more collateral assets. Interest rates adjust dynamically based on utilization, creating a self-balancing market for short-term stablecoin credit.
dUSD, forked from Aave V3. It serves as the credit engine of the ecosystem, enabling dUSD lending and borrowing activity to take place on Fraxtal (and soon, Ethereum). Similar to Aave, dLEND is a multi-collateral money market, where lenders earn yield by supplying dUSD into a shared pool while others borrow dUSD from that pool by supplying one or more collateral assets. Interest rates adjust dynamically based on utilization, creating a self-balancing market for short-term stablecoin credit.
 dUSD, forked from Aave V3. It serves as the credit engine of the ecosystem, enabling dUSD lending and borrowing activity to take place on Fraxtal (and soon, Ethereum). Similar to Aave, dLEND is a multi-collateral money market, where lenders earn yield by supplying dUSD into a shared pool while others borrow dUSD from that pool by supplying one or more collateral assets. Interest rates adjust dynamically based on utilization, creating a self-balancing market for short-term stablecoin credit.
dUSD, forked from Aave V3. It serves as the credit engine of the ecosystem, enabling dUSD lending and borrowing activity to take place on Fraxtal (and soon, Ethereum). Similar to Aave, dLEND is a multi-collateral money market, where lenders earn yield by supplying dUSD into a shared pool while others borrow dUSD from that pool by supplying one or more collateral assets. Interest rates adjust dynamically based on utilization, creating a self-balancing market for short-term stablecoin credit.In addition to the existing V3 features and mechanics which can be referenced through Aave’s documentation, dLEND’s key differentiator lies in its ability to actively subsidize dUSD borrowers with interest rebates.
User Benefits
- Borrowers still pay a Gross Borrow APY when taking dUSD loans from dLEND, but they also earn rebates which help lower the Net Borrow APY, enabling cheaper access to credit.
- Yield loopers who borrow dUSD may capture carry trade opportunities more efficiently thanks to subsidized credit. Additionally, subsidized loopers don’t need as much leverage to achieve similar returns on the same collateral vs. unsubsidized loopers, allowing them to reduce risk exposure.
- Lenders who supply dUSD into dLEND earn
dT Points and high organic yield thanks to subsidy-driven credit demand and utilization. Lending deposits are also over-collateralized to minimize credit and liquidation risks.
- Stakers who supply dUSD into the
sdUSD vault earn dT Points and organic yield from dLEND as well, with additional benefits from composability and secondary market liquidity.
For user instructions and current opportunities, please refer to User Guide.
Risk Management
dTRINITY adopts conservative protocol parameters and policies that prioritize safety for dUSD lenders and sdUSD holders over borrower flexibility, including:
- Disabling collateral rehypothecation in dLEND by default to mitigate bad liquidations and nested leverage risk. This makes dUSD the only borrowable asset in dLEND.
- Disabling dUSD as a collateral to borrow against itself, mitigating recursive lending and subsidy arbitrage risk. For this same reason, sdUSD is not accepted as a collateral in dLEND.
- Capping Max LTV (loan-to-value) thresholds between 60-80% in dLEND, enabling 5X leverage at most for borrowers.
- Setting Liquidation LTV (LLTV) thresholds at 5 percentage points above Max LTV, providing 15-35% LTV in collateral liquidation buffer.
- Isolating collateral pools across chains to mitigate network-specific risk. This means liabilities are also isolated across chains, and collateral supplied on one chain cannot be used to cover debt on other chains.
- Limiting collateral support to only assets from proven projects with strong credibility, transparency, adoption, and track records.
Collateral Assets
dLEND’s collateral pools only support the largest and most liquid assets from:
- Established issuers and protocols already whitelisted for inclusion in dUSD’s reserves.
- Aave’s collateral pool on Ethereum, including crypto, stablecoins, yieldcoins, liquid staking tokens (LST), liquid restaking tokens (LRT), Pendle principal tokens (PT), and tokenized real-world assets (RWA). This approach allows dLEND and sdUSD to mirror Aave’s proven risk curation standards with a more selective asset selection filter.
- Frax on Fraxtal, including WFRAX, frxUSD, sfrxUSD, frxETH, sfrxETH, and Frax Bonds (FXBs).
To view currently supported collateral, visit app.dtrinity.org/dlend/money-markets.
Price Oracles
dLEND integrates third-party oracles like Api3 and Chainlink as well as direct feeds from asset issuers to value collateral deposits and manage liquidations. Additional oracle providers may be integrated over time to improve redundancy and reliability.
Oracle Methodology
In dLEND, dUSD’s price is hard-coded at $1 to:
- Minimize oracle-related risk without impacting lending operations, since dUSD is disabled as a collateral to secure loans by default.
- Prevent borrowing capacity manipulation on dLEND when dUSD trades above $1.
- Enable loan repayments at face value on dLEND when dUSD trades below $1, thereby incentivizing borrowers to arbitrage and restore price stability.
Additionally, to enhance pricing accuracy, oracles for yield-bearing collateral (typically ERC-4626 vault tokens) rely on composite feeds to calculate the underlying value rather than exchange-traded prices alone, mitigating potential risk from market liquidity issues.

Examples
- sfrxUSD Price = sfrxUSD/frxUSD × frxUSD/USD
- sfrxETH Price = sfrxETH/frxETH × frxETH/ETH × ETH/USD
Collateral Liquidation
Borrowers are liquidated if their LTV ratio exceeds the predefined LLTV threshold, which varies by collateral. This is tracked via the borrower’s Health Factor, where a value of less than 1 would start triggering liquidation. To avoid liquidation, borrowers can increase their Health Factor by supplying additional collateral, partially repay, or fully repay outstanding debt.
Health Factor Methodology
Since a borrower can supply multiple collateral, each collateral’s value is weighted by its own LLTV. The sum of those weighted values is divided by the borrower’s total debt to determine the Health Factor.

Permissionless Liquidations
dLEND’s liquidation mechanism is similar to Aave’s, where up to a specific percentage of a borrower's collateral (typically 50%) is seized and sold to partially repay debt once the Health Factor drops below 1. Like on Aave, liquidations on dLEND are permissionless and can be executed by any market participant, i.e., liquidators.
Liquidators can repay a portion of the borrower's outstanding debt and, in return, receive a discounted portion of the collateral. They earn a liquidation penalty from the borrower which varies by market (typically 5%), providing a strong economic incentive to help the protocol maintain solvency. Liquidators can also utilize dUSD flash loans to execute liquidations without upfront capital, further enhancing efficiency and responsiveness in volatile market conditions.
Interest Rate Model
dLEND’s interest rate model governs how dUSD credit is priced based on the supply and demand equilibrium between lenders and borrowers. By embedding borrower subsidies into this framework, dLEND introduces a demand-side stimulus that enables the protocol to sustain utilization, increase capital efficiency, and deliver superior rates to both sides of the market.
Rates Methodology
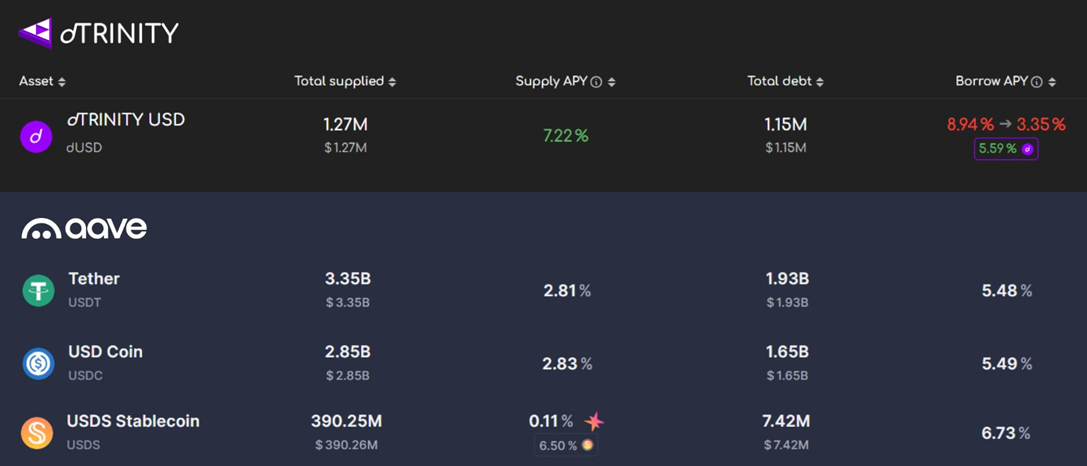
dLEND uses the standard dynamic interest rate model forked from Aave V3. Like stablecoins in Aave, the Supply APY and Borrow APY of dUSD are variable rates that adjust in real time based on credit utilization. However, dLEND introduces a key innovation: recurring interest rebates for dUSD borrowers, represented as the Rebate APY (paid in dUSD). These subsidies are funded exogenously by dUSD’s float revenue and distributed pro-rata to borrowers based on their outstanding debt. As a result, dLEND’s interest rate curve for dUSD behaves differently than Aave’s curves for USDC, USDT, etc.

To view the current interest rate model, please visit the dLEND dUSD market. For more details on Rebate APY calculations, please refer to Stablecoinomics 101.
Subsidized Borrowing Cost
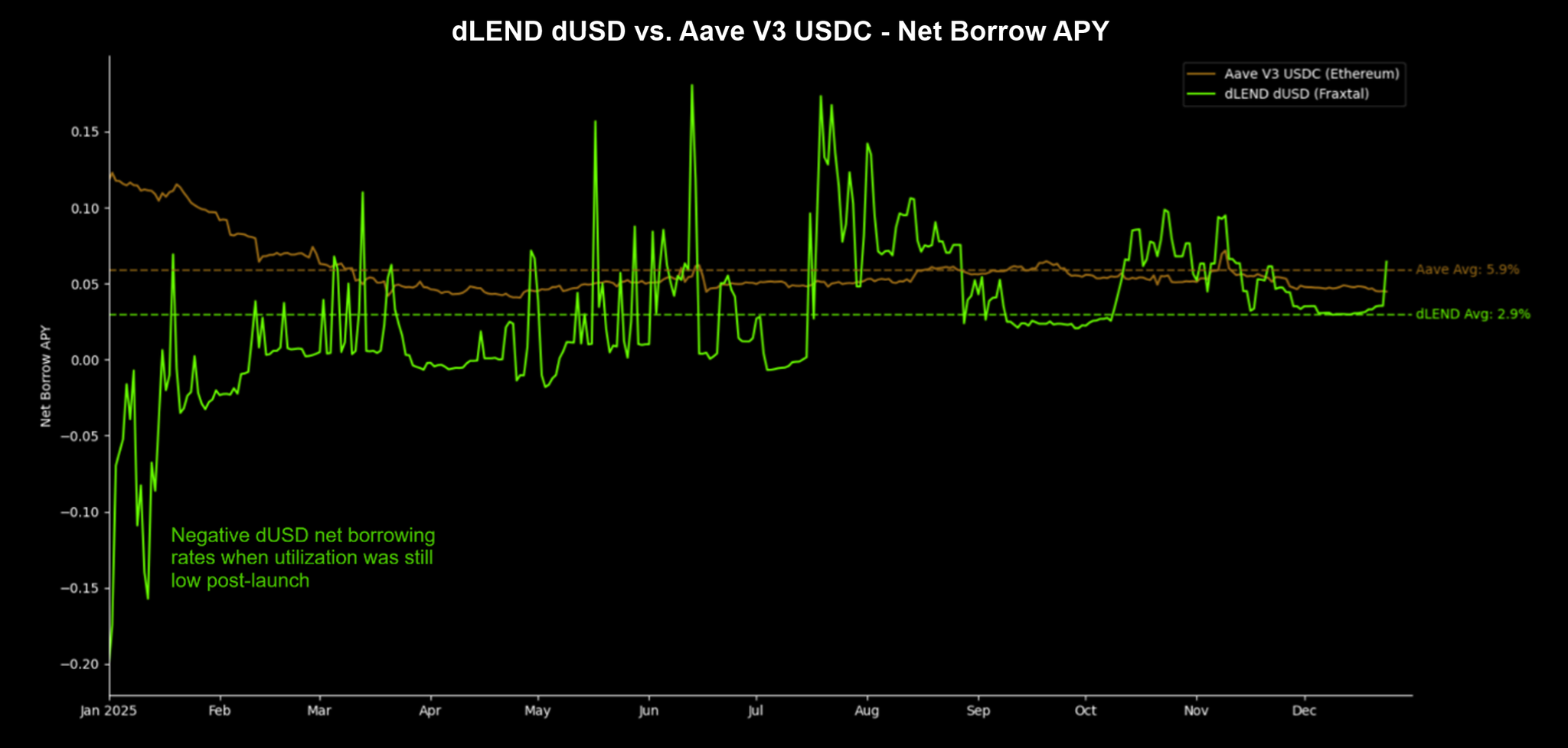
Borrowers with active dUSD loans can claim interest rebates which are paid out separately in real-time, not automatically deducted against gross interest accrual. If borrowers claim rebates to pay off interest, they can reduce dUSD’s Net Borrow APY, enabling below-market average borrowing rates.
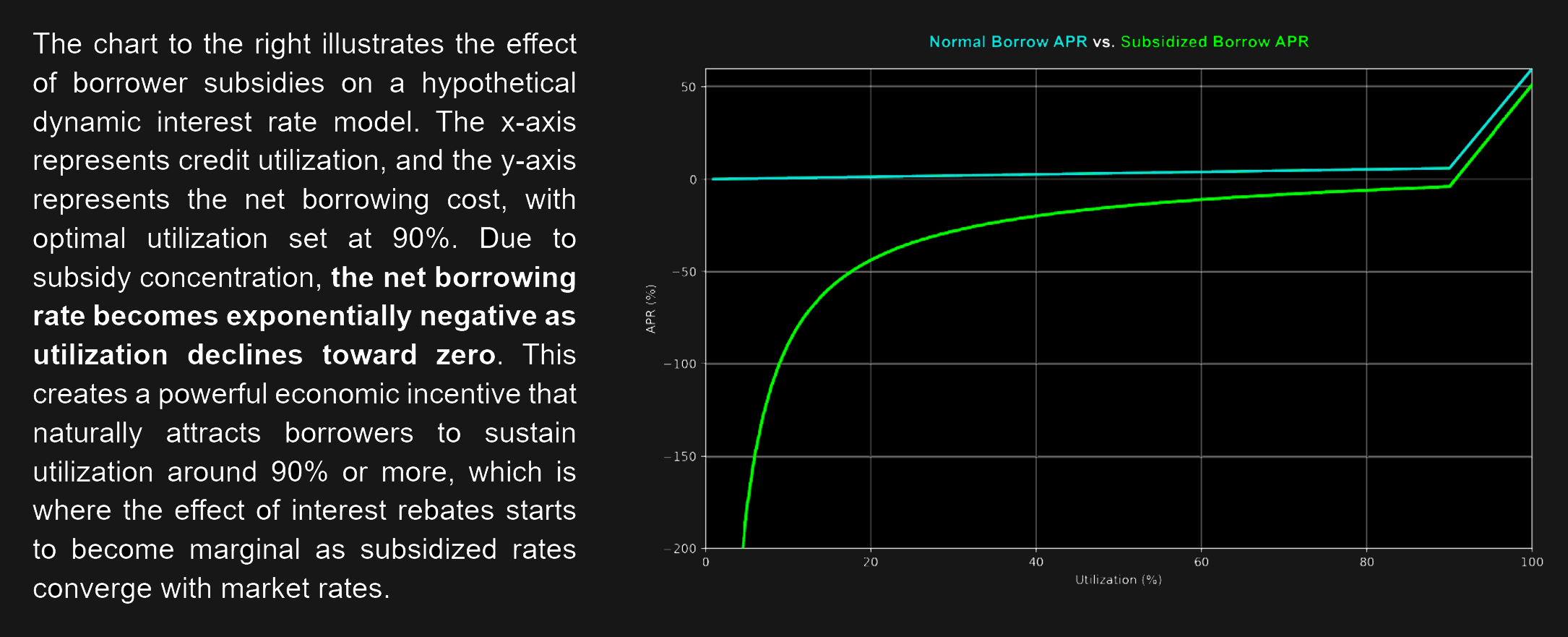
- When utilization is low, subsidy concentration may occur due to less outstanding debt vs. available rebates, further increasing their marginal benefit. This may even produce net negative interest rates, where users are effectively paid to borrow.
- Conversely, subsidy dilution may occur at higher utilization, reducing rebates and their marginal benefit. This helps align the Net Borrow APY with market rates while naturally discouraging excess leverage when utilization reaches optimal levels.
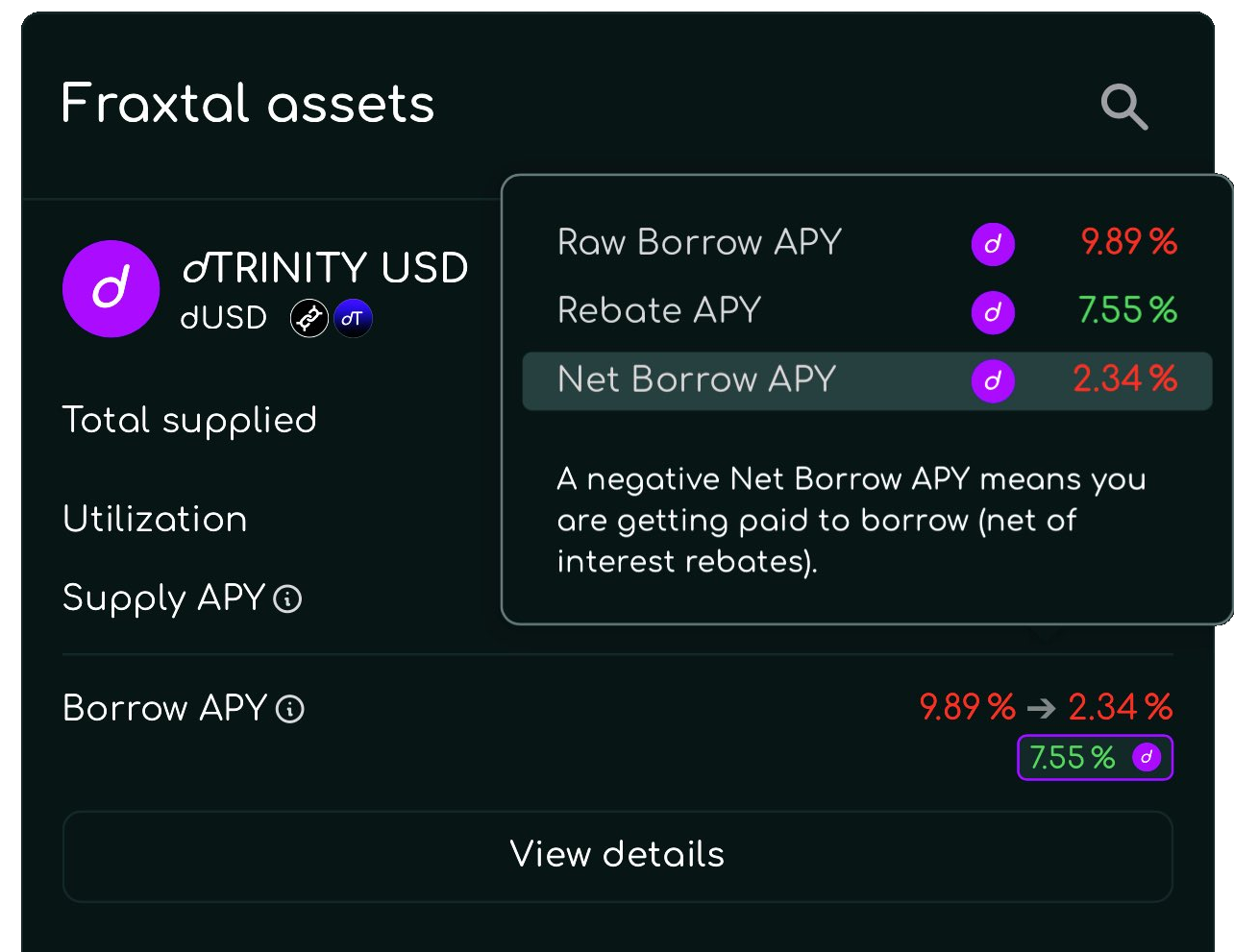
In 2025, dLEND dUSD borrowers outperformed market rates on 73% of days, with an average daily Net Borrow APY of 2.9%—half of Aave USDC’s 5.9%.
Structurally Higher Utilization
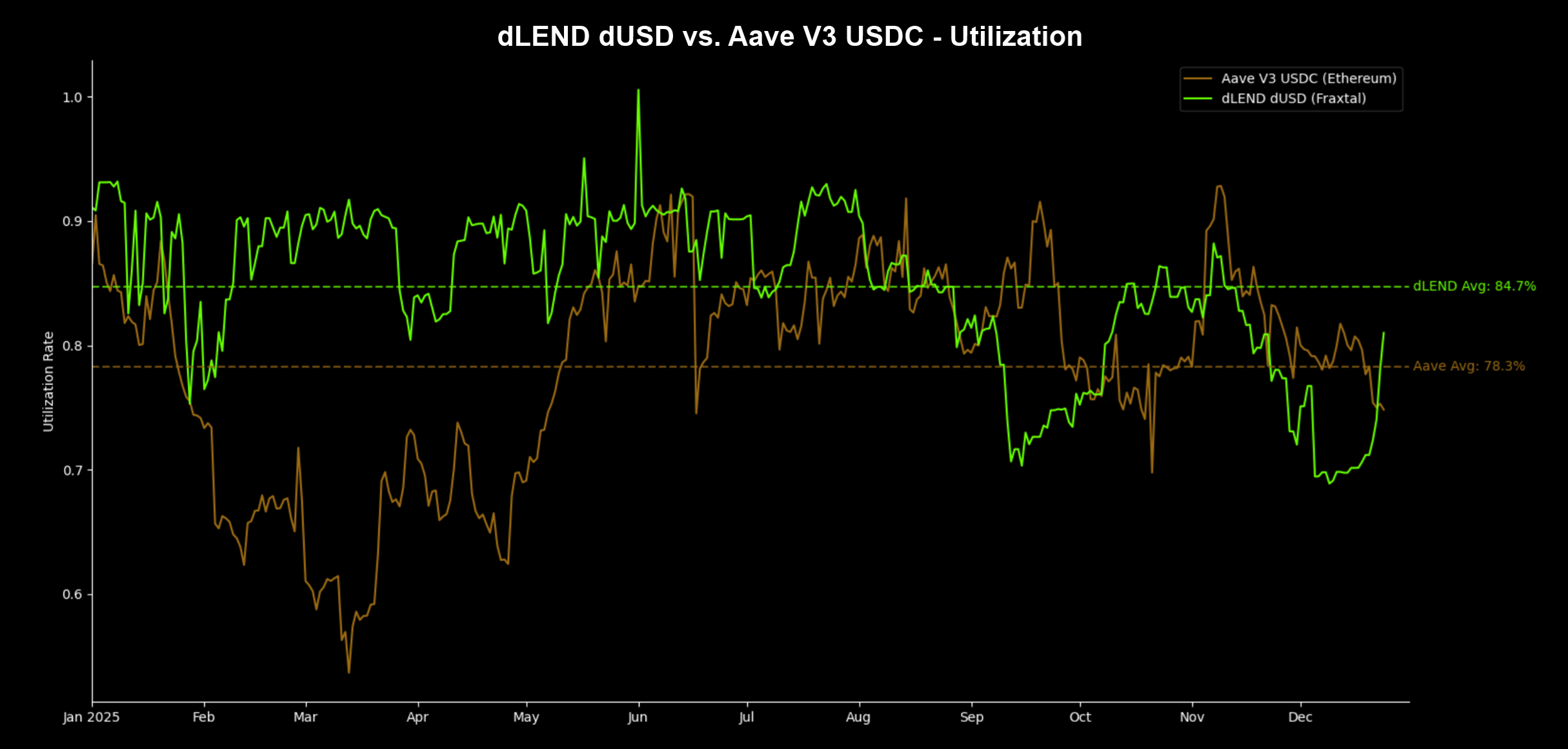
Since borrowers respond rationally to incentives, subsidized lending markets can accelerate and sustain credit utilization much more efficiently than unsubsidized markets.
In 2025, dLEND dUSD achieved 84.7% average daily utilization vs. 78.3% for Aave USDC, outperforming on 70% of days. Although utilization declined market-wide due to bearish conditions in Q3-Q4, dLEND dUSD achieved consistently high utilization between 85-90% during the first half of the year, when market appetite for credit was still strong. This confirms in practice that borrower subsidies structurally anchor credit demand toward higher average utilization.
Enhanced Lending Yield
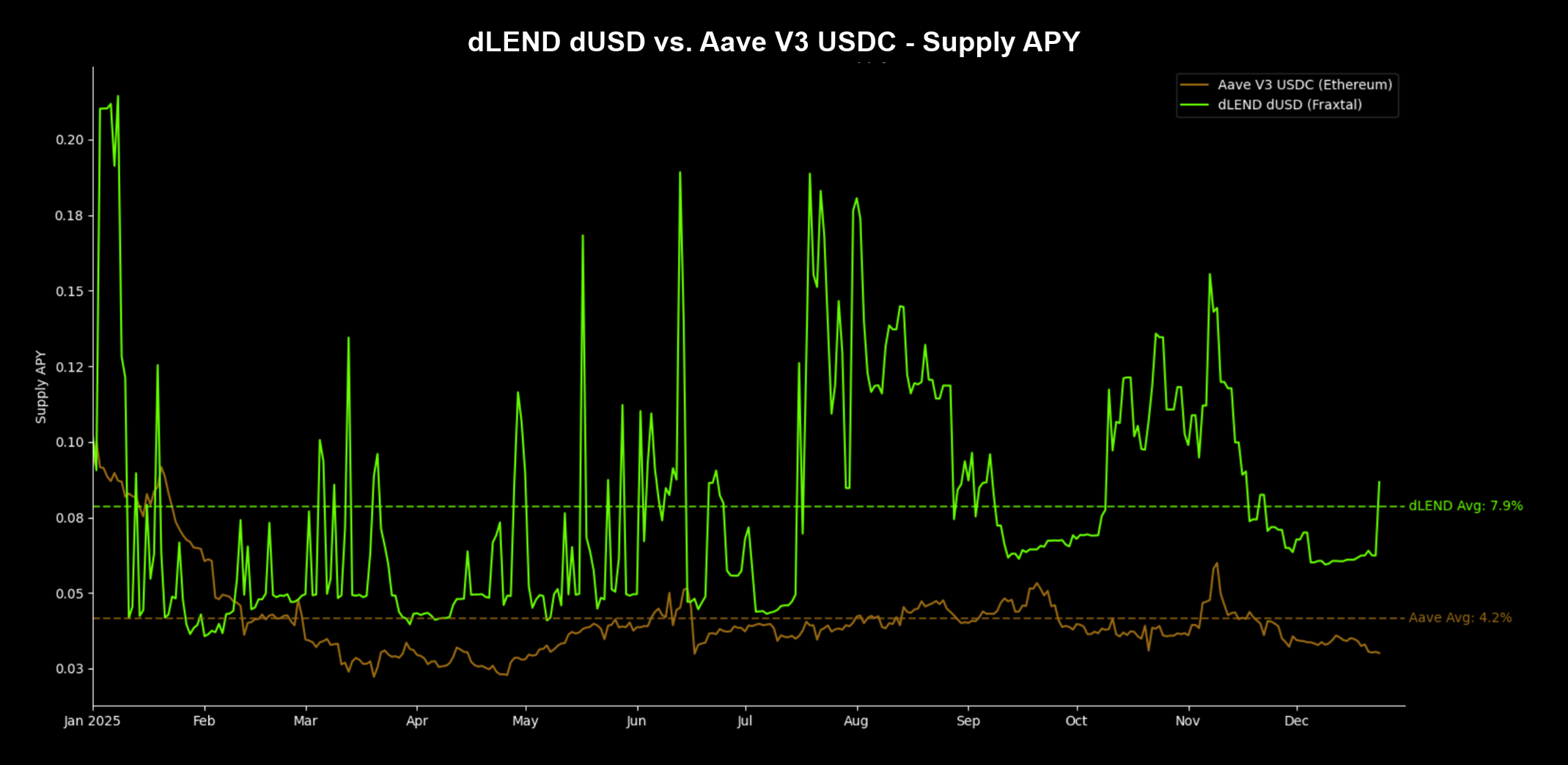
As utilization rises toward optimal levels, dLEND’s dynamic interest rate model increases dUSD’s gross rates organically, producing above-market average lending yields. Subsidized credit also allows dLEND dUSD to consistently deliver a higher Supply APY vs. Net Borrow APY, a rarely seen phenomenon in traditional lending models, where borrowing rates are almost always higher than lending rates.
In 2025, dUSD lenders outperformed market rates on 91% of days, capturing an average daily Supply APY of 7.9%—an 88% outperformance vs. Aave USDC’s 4.2%.
Efficient Yield Looping
When dLEND dUSD utilization is below optimal levels, subsidy concentration and lower gross borrowing costs may enable positive carry trade opportunities for loopers who rely on cheap leverage to amplify yield generation. Thanks to subsidized loans, loopers who borrow dUSD not only improve net P&L per unit of debt, they also require less leverage to achieve similar returns on the same collateral vs. unsubsidized loopers.
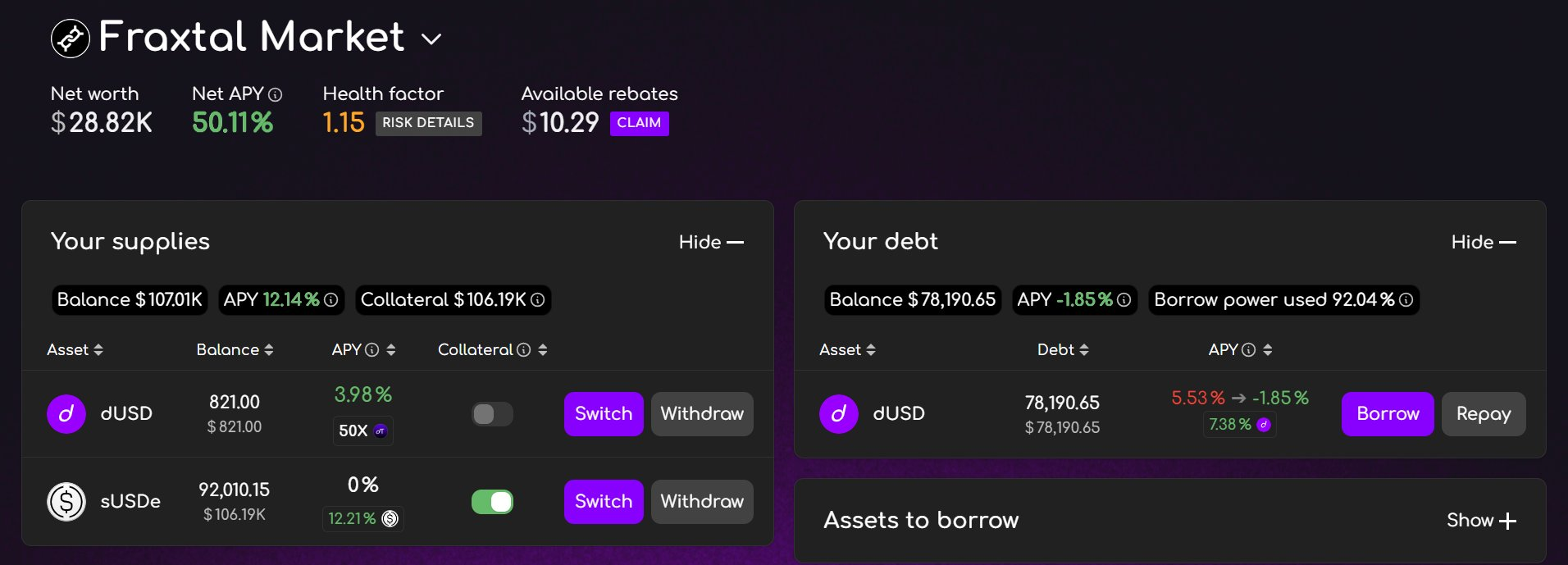
In the screenshot below, a looper on dLEND financed their sUSDe collateral using subsidized dUSD debt, achieving a 50.1% Net APY with about 3.7X leverage at roughly 74% LTV. Without borrower subsidies, the same position would have earned only about 30% Net APY at that leverage. To reach a 50% Net APY without subsidies, the looper would have needed roughly 6.7X leverage, pushing the position to over 85% LTV while increasing liquidation risk.